elisa test technique|difference between elisa and immunoassay : ODM ELISA, short for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, is a widely used laboratory technique that detects and measures the presence of specific antibodies or antigens in a sample. It involves the binding of target molecules (antibodies or antigens) to a solid surface, followed by the addition of enzymes or fluorescent markers to generate a detectable signal. $185.99
{plog:ftitle_list}
If you're looking for professional, fast, and reliable autoclave repair, contact Hayes Handpiece Inc. today. Our team is ready to assist with your autoclave equipment repair and Replacement services to ensure smooth operations at .
how does an elisa work
Enzyme immunoassays (EIAs) use the catalytic properties of enzymes to detect and quantify immunologic reactions. Enzyme-linked .
ELISA, short for Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay, is a widely used laboratory technique that detects and measures the presence of specific antibodies or antigens in a sample. It involves the binding of target molecules (antibodies or antigens) to a solid surface, followed by the addition of enzymes or fluorescent markers to generate a detectable signal.Introduction: ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a technique for detecting the presence of antigens in biological materials. An ELISA, like other types of immunoassays, uses antibodies to detect a target antigen via highly specific antibody-antigen interactions. What is ELISA? The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an antibody-based technique for the detection and quantification of target analytes in solution. The targets are typically proteins, for example, cytokines, chemokines, immunoglobulins, hormones, and other biomarkers. ELISA setups include direct/indirect (antigen first), competitive, and sandwich .
biochimie sanguine
how do elisa assay work
ELISA is so named because the test technique involves using an enzyme system and immunosorbent. ELISA consists of antibodies bonded to enzymes; the enzymes remain able to catalyze a reaction, yielding a visible end product. The term enzyme-linked refers to an enzyme’s covalent binding to an antibody.
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, also called ELISA or EIA, is a test that detects and measures antibodies in your blood.This test can be used to determine if you have antibodies related to .Explanation: ELISA assay technique involves a number of steps. However, calculation of results and observations are two of the most important concluding steps of ELISA. There are different sections under which the output can be framed. These are as follows: 1) Quantitative (includes standard curve graph by knowing the concentration of antigen .The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a technique that uses antibodies to specifically detect and quantify the amount of a target antigen in a liquid sample. ELISAs are distinct from other antibody-based methods in that the antibody-epitope interaction occurs with one component immobilized to a solid surface, typically a multi-well . The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a common laboratory technique used to measure the concentration of an analyte like antibodies or antigens in solution. It works by using the principle of antigen-antibody binding and an enzyme-linked secondary antibody or antigen to detect the presence of an analyte.
ELISA assay - This immunological assay lecture explains about the elisa test procedure and principle behind the elisa assay including direct, indirect and sa.
ELISA test stands for Enzyme–Linked Immunosorbent Assay. It is a type of serological test and immunoassay technique. In the ELISA test, an enzyme links to the antibodies particularly to detect the presence of proteins like antigens. The ELISA method was evolved from the RIA technique in . Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technique . used to d etect an antigen in a given sample. A. The antigen (in liquid . phase) is added to t he wells, w here it a dheres to the walls.ELISA ELISA - an acronym for Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay. The ELISA assay is a widely used biochemical assay to detect in a sample the presence of and quantity of proteins, such as hormones and antibodies and bacteria or viruses. The ELISA assay uses the coupling of antigens and antibodies and relies on the specificity and affinity of antibodies for antigens.
3. INTRODUCTION ELISA(Enzyme Linked ImmunoSorbent assay) is a widely used technique for detection of antigen (Ag) or antibody(Ab). The technique was developed in 1971 by Peter Perlmann and Eva Engvall at Stockholm University, Sweden. A technique to prepare something like immunosorbent to fix antibody or antigen to the surface of a container .Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is one of the most specific and straightforward assays for detecting biomolecules in research and clinics. With advances in analytical methods, ELISA assay has been constantly optimized to improve its sensitivity, and different types of ELISA are now availab . ELISA is a plate based assay technique which is used for detecting and quantifying substances such as peptides, proteins, antibodies and hormones. An enzyme conjugated with an antibody reacts with colorless substrate to generate a colored product. Such substrate is called chromogenic substrate. A number of enzymes have been used for ELISA such .
biochemical analysis report
ELISA is a widely used laboratory technique for detecting and quantifying biomolecules with high sensitivity and specificity. In food safety testing, ELISA plays an important role in reliably detecting contaminants such as mycotoxins and allergens, ensuring product safety, maintaining product integrity, and verifying compliance with labeling regulations.
This video describes the concept behind ELISA in a simple manner. Also, it describes the use and variants of ELISA.ELISA | Enzyme linked immonosorbent assay .
ELISA stands for enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, also often referred to as enzyme immunoassay (EIA). An ELISA, like other types of immunoassays, relies on antibodies to detect a target antigen using highly specific antibody-antigen interactions. In an ELISA assay, the antigen must be immobilized to a solid surface.
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is an immunological technique extensively used in research and clinical laboratory settings to quantitatively identify a specific protein (i.e., the antigen or biomarker) in a biological matrix while relying on the principle of the specific binding interaction between the antigen and the antibody against the antigen of interest . A competitive ELISA, also known as an inhibition ELISA or blocking ELISA, is possibly the most complex of the ELISA techniques. Originally developed in 1976 7 for the detection of human choriogonadotropin, the assay works by detecting interference to an expected output signal level, producing an inverse relationship. The Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is one of the most sensitive immunoassays available. The typical detection range for an ELISA is 0.1 to 1 fmole or 0.01 ng to 0.1 ng. It is a plate-based assay technique designed for detecting and quantifying peptides, proteins, antibodies, and hormones. 3. • ELISA is a plate based assay technique which is used for detecting and quantifying substances such as peptides, proteins, antibodies and hormones. • An enzyme conjugated with an antibody reacts with colorless substrate to generate a colored product. Such substrate is called chromogenic substrate.
HBsAg ELISA: The Test. HBsAg ELISA is a laboratory test used to detect the presence of HBsAg in a patient’s serum or plasma. The test is based on the principles of immunology and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) technology. It is a highly sensitive and specific method for identifying individuals infected with the Hepatitis B virus.The ELISA Assay - The Enzyme-Linked ImmunoSorbent Assay, or ELISA, is a sensitive laboratory technique that uses antibodies to detect the presence of specific molecules (i.e. peptides, proteins, or hormones) in a complex sample. These samples can be single proteins or complex mixtures like cellular lysates.
The enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is a powerful method for detecting and quantifying a specific protein in a complex mixture. Originally described by Engvall and Perlmann (1971), the method enables analysis of protein samples . Pierce (1967) developed methods to chemically link antibodies to biological enzymes whose activities . I make animations in biology with PowerPoint, this animated video is about Direct ELISA Test. Which is a plate-based assay technique designed for detecting a.Enzyme-linked immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) is a technique used to quantitatively detect an antigen within a sample such as peptides, blood samples, antibodies and hormones, cell lysates, and food items. ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) is a method used to quantitatively detect an antigen within a sample.
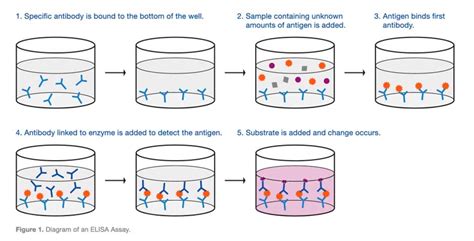
elisa test steps
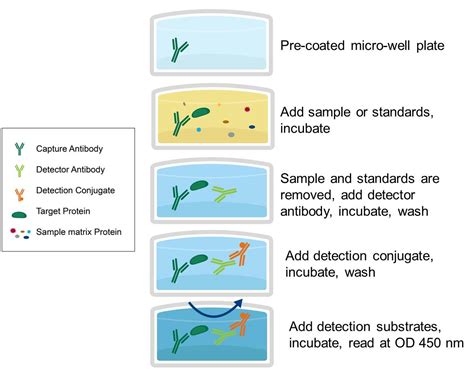
Hydrothermal autoclaves are widely used in quartz crystal growth. Distribution of temperature, quartz concentration and flow structure in the upper chamber containing crystal seeds influence the quality of grown crystal.
elisa test technique|difference between elisa and immunoassay